What makes Zamak suitable for precision die casting?
Dimensional Accuracy and Fluidity
Zamak alloys are engineered specifically to deliver the precision and repeatability required in advanced zinc die casting. Their excellent fluidity enables molten metal to fill intricate molds with fine details and thin walls, allowing for high-definition geometries that would be difficult to achieve with aluminum die casting or magnesium alloy casting. This fluid behavior is critical in parts for locking systems and consumer electronics, where dimensional tolerances are extremely tight.
The low solidification shrinkage of Zamak minimizes internal voids and distortion, making it ideal for precision components such as housings, mechanical connectors, and micro-mechanisms. Combined with CNC machining prototyping, engineers can verify tolerances in pre-production stages and adjust mold geometry to achieve micron-level consistency.
Manufacturing Process Efficiency
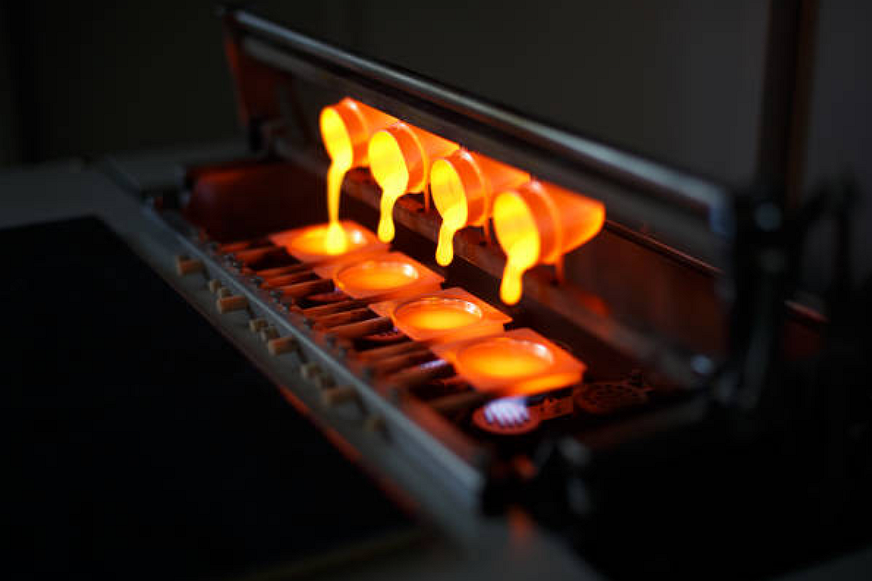
Zamak’s melting range, around 380–420°C, contributes to faster cycle times and lower thermal stress on tooling compared to higher-temperature alloys. This property extends mold life and enhances throughput in die casting manufacturing. When integrated with gravity casting and rapid molding prototyping, the result is a highly efficient process capable of producing thousands of near-net-shape components daily.
In precision-driven sectors such as automotive and e-mobility, this combination of speed and accuracy is crucial for meeting large-scale production demands while maintaining part uniformity.
Material Properties That Ensure Precision
Zamak’s balanced composition of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, and copper provides outstanding mechanical stability and surface finish. Alloys such as Zamak 3, Zamak 5, and Zamak 7 exhibit excellent dimensional repeatability, along with high tensile and impact strength. Their fine-grain structure resists deformation during ejection, ensuring that precision tolerances are maintained across thousands of cycles.
Additionally, Zamak’s natural corrosion resistance reduces the need for heavy post-processing. When combined with advanced coatings and injection molding integration, it enables the manufacture of hybrid parts that require precise metal-to-plastic alignment.
Surface Treatment for Enhanced Accuracy
Post-casting surface quality plays a major role in precision applications. Zamak responds exceptionally well to finishing processes, such as chrome plating and powder coating, which enhance durability and visual uniformity. These surface treatments maintain tight dimensional control without significantly altering the surface geometry, a key factor in achieving aesthetic or functional precision in parts.
Industries such as power tools, telecommunications, and energy systems often specify Zamak for high-accuracy components that are exposed to mechanical stress and environmental variations.
Conclusion
Zamak’s superior flow characteristics, mechanical strength, and compatibility with modern manufacturing techniques make it one of the most reliable materials for precision die casting. Its balance of accuracy, repeatability, and surface finish excellence enables manufacturers to achieve both efficiency and performance across diverse industries.