Beauty Meets Function: Elevating Product Design with Over Molding Aesthetics
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, overmolding is a technique that seamlessly merges aesthetics with functionality. Industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices increasingly rely on overmolding to produce visually appealing, ergonomic, and highly durable products. By enhancing both form and function, manufacturers can boost marketability and foster stronger brand loyalty.
Understanding Over Molding
Overmolding is an advanced form of plastic injection molding, which involves molding one material onto another substrate, typically combining rigid plastics or metals with softer, flexible materials such as silicone rubber or thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs). Unlike traditional injection molding, this approach allows manufacturers to create unified, multi-material components with superior aesthetic appeal and improved functional performance.
The Aesthetic Advantages of Overmolding
Enhanced Visual Appeal
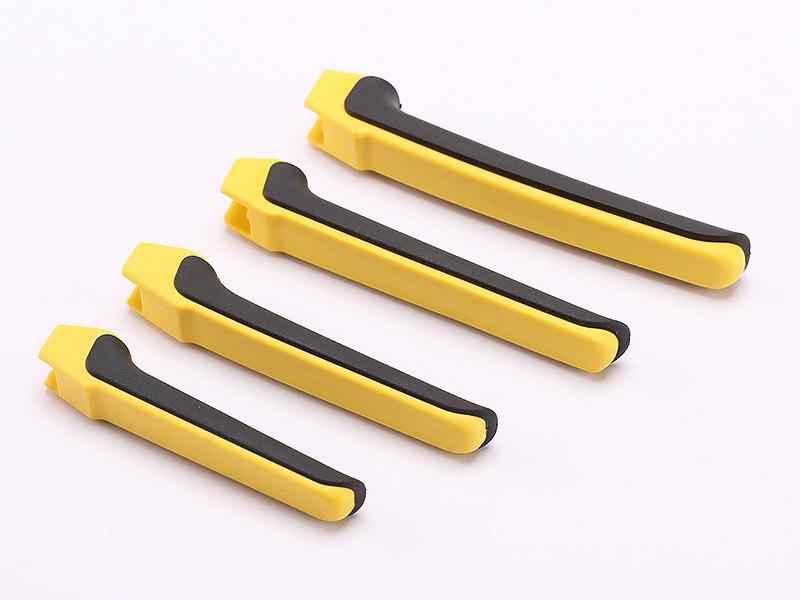
Overmolding provides endless design possibilities, allowing products to feature vibrant colors, diverse textures, and luxurious finishes. Integrating materials like silicone or elastomers adds an attractive soft-touch surface, significantly elevating a product’s perceived quality and attractiveness to consumers.
Improved Ergonomics and Comfort
Products featuring over-molding, especially using materials like TPU, offer enhanced tactile experiences, ergonomic benefits, and greater user comfort. This is particularly valuable in handheld or wearable applications, as it influences consumer purchasing decisions.
Customized Branding Opportunities
Overmolding enables the seamless integration of branding elements, such as colors, textures, or logos, directly into product designs, effectively strengthening brand identity and differentiation.
Functional Benefits Complementing Aesthetics
Increased Product Durability
Overmolding adds protective layers, significantly increasing resistance to impact, environmental exposure, and wear. This added durability ensures products remain aesthetically appealing and functionally robust, enhancing their lifespan.
Enhanced Grip and Safety
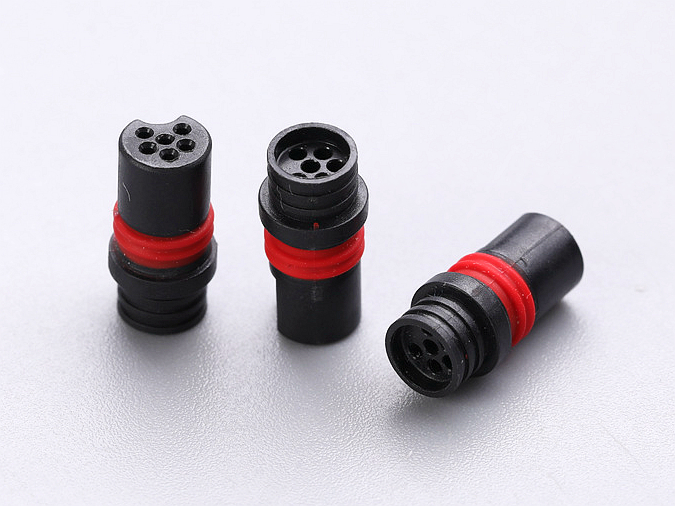
Soft, textured over-molded surfaces significantly enhance user grip, thereby improving product safety and usability. This benefit is essential for tools, medical devices, and consumer electronics, where secure handling is crucial.
Improved Vibration and Noise Reduction
The elastomeric materials commonly used in overmolding effectively absorb vibrations and dampen noise, thereby enhancing product reliability and user satisfaction, which is especially important in automotive and industrial applications.
Choosing Materials for Optimal Overmolding Results
Material selection is crucial to the success of overmolding. Commonly used materials include thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), TPU, and silicone rubber, each providing unique advantages:
TPE: Flexible, cost-effective, easy to mold, ideal for ergonomic applications.
TPU: High durability, chemical resistance, excellent tactile feel.
Silicone Rubber: Outstanding thermal stability, biocompatibility, and soft-touch aesthetics.
Strategically balancing these factors ensures optimal aesthetic appeal and functionality without unnecessary expense.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Consumer Electronics Sector
Manufacturers extensively employ overmolding in consumer electronics, including smartphone cases and wearables. Utilizing materials like TPE, companies produce visually appealing, ergonomic products with enhanced durability, which significantly influences consumer preferences.
Automotive Industry
In automotive applications, over-molded components, including steering wheels, dashboard elements, and control knobs, significantly enhance both aesthetic appeal and ergonomics, ultimately improving the user experience. Automotive manufacturers utilize overmolding to craft luxurious interior components that enhance perceived product value and market competitiveness.
Medical Device Industry
Medical device manufacturers widely utilize overmolding for products such as ergonomic surgical handles and diagnostic tools. Materials such as medical-grade silicone enhance user comfort, grip, and safety, meeting strict medical standards while significantly improving patient and practitioner experiences.
Key Design Considerations for Successful Overmolding
Precise Mold Design and Material Compatibility
Efficient mold design and selecting compatible materials are crucial. This approach prevents defects, enhances aesthetics, and improves overall product performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Integration of Color and Texture
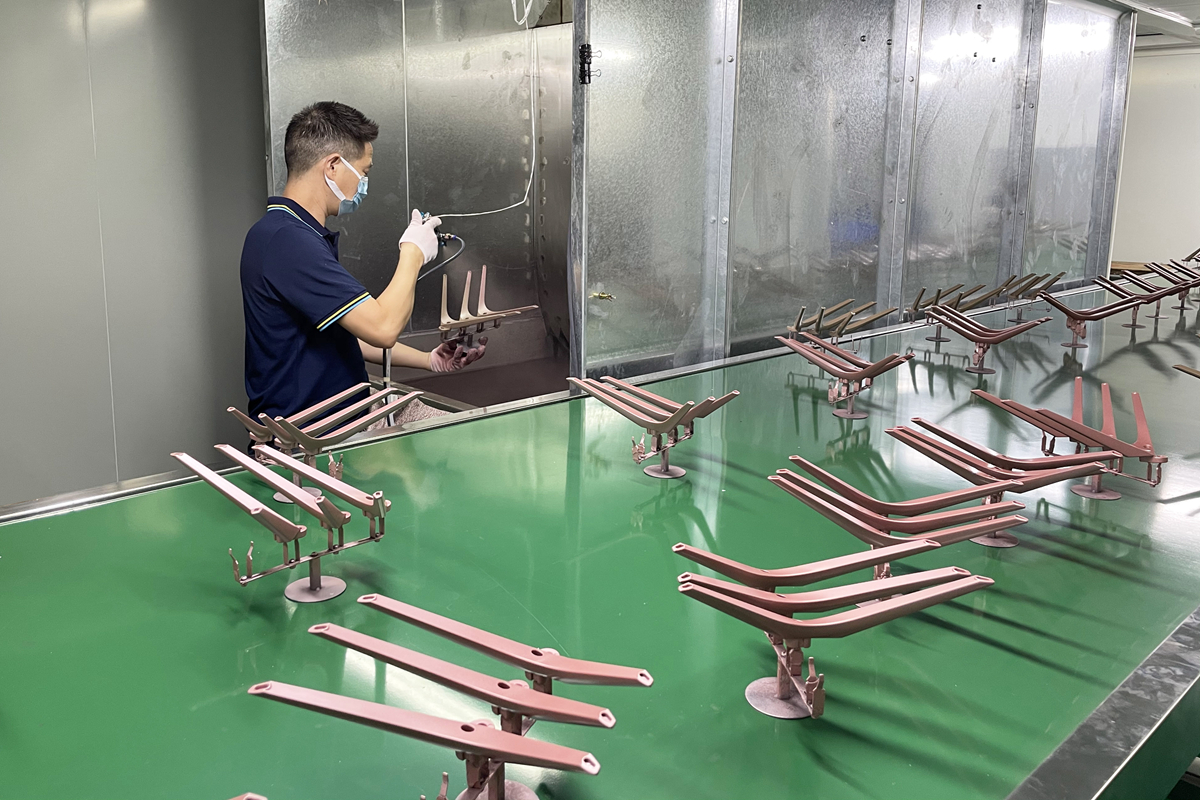
Careful selection of color palettes and surface textures enables manufacturers to align product aesthetics with their brand identity, thereby increasing market appeal and fostering consumer loyalty.
Automation for Quality and Consistency
Automating overmolding through robotics and intelligent monitoring ensures consistency, reduces production costs, and maintains superior aesthetic and functional standards.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Overmolding
Ensuring Robust Material Bonding
Selecting compatible substrates, such as ABS, ensures effective bonding, reduces failures, and maintains product integrity throughout its lifetime.
Controlling Production Costs
Effective production management, optimized mold design, and strategic material selections help manufacturers maintain budget efficiency without sacrificing product quality or aesthetics.
Achieving Consistent Aesthetics at Scale
Implementing stringent quality assurance measures and automated processes ensures consistent aesthetic quality, which is essential for maintaining a brand's reputation and reducing production inconsistencies.
Future Trends in Overmolding Aesthetics
Innovative Material Developments
Continued research into advanced, sustainable, and eco-friendly materials presents significant opportunities for enhanced aesthetic and performance outcomes in over-molded products, aligning with growing consumer preferences.
Integration of Smart Technologies
Future trends indicate the incorporation of smart technologies, including responsive materials and interactive surfaces, significantly enhancing consumer interaction and product attractiveness through innovative functionalities.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Choices
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting recycled and biodegradable materials in response to consumer demand for sustainable solutions. Overmolding will evolve toward environmentally responsible material selection, reinforcing consumer trust and brand reputation.
Conclusion
Overmolding offers manufacturers a sophisticated approach to integrating beauty and function, significantly enhancing product design, ergonomics, durability, and marketability. As industries embrace the aesthetic advantages and functional benefits of overmolding, they can effectively differentiate their products, achieve enhanced consumer satisfaction, and secure a sustained competitive advantage in evolving marketplaces.