Which industries can benefit most from eco-friendly Zamak die casting?
Automotive Industry: Lightweight and Recyclable Precision Components
The automotive industry is one of the largest beneficiaries of eco-friendly zinc die casting. Zamak alloys, renowned for their strength and dimensional accuracy, facilitate the production of intricate components, including door handles, interior fittings, and precision connectors, with minimal post-processing requirements. The low melting temperature of Zamak drastically reduces energy consumption compared to aluminum die casting, lowering the carbon footprint per part.
Additionally, high recyclability ensures that offcuts and scrap from precision casting are easily reused. Components made from Zamak 3 or Zamak 5 provide excellent mechanical stability, corrosion resistance, and finish quality—key factors for sustainable vehicle manufacturing that meet global environmental standards.
Consumer Electronics: Miniaturization with Material Efficiency
In consumer electronics, Zamak alloys enable the production of miniaturized yet durable housings and connector components. Their superior castability enables the molding of thin-walled parts with tight tolerances, thereby eliminating the need for excessive machining. Using insert molding or overmolding with Zamak inserts enables the creation of hybrid metal-plastic structures, combining lightweight performance with aesthetic design.
Zamak’s thermal conductivity is advantageous for heat dissipation in compact devices, reducing the need for separate cooling systems. Environmentally friendly finishes, such as powder coating or electropolishing, enhance corrosion resistance and visual quality without the use of toxic chemicals, aligning with eco-compliance in consumer product manufacturing.
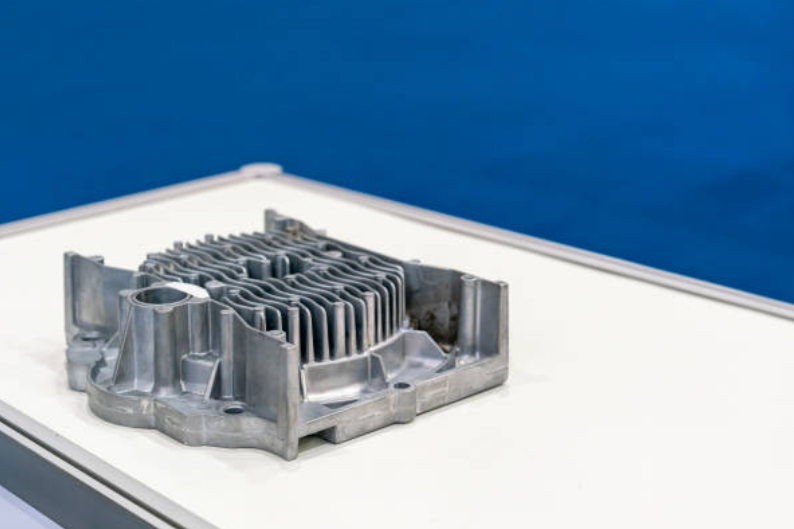
Lighting and Energy Systems: Long Life and Recyclability
The lighting solution and energy sectors leverage Zamak’s excellent heat conduction and surface finish properties to produce efficient housings, brackets, and structural frames. The alloys’ ability to maintain mechanical integrity under thermal cycling makes them ideal for LED and renewable energy systems, where longevity directly contributes to sustainability.
Through high material yield in gravity casting and sand casting, manufacturers reduce waste during large-scale production. Using recyclable zinc alloys further supports circular manufacturing, as components can be reprocessed multiple times with minimal energy input.
Medical and Precision Device Manufacturing
In medical device production, Zamak’s precision and biocompatibility (after suitable finishing) make it suitable for ergonomic housings, testing instrument parts, and durable mechanical assemblies. When paired with advanced processes like CNC machining prototyping or 3D printing prototyping, Zamak allows engineers to design lightweight, long-lasting parts with excellent repeatability and minimal environmental impact.
Moreover, sustainable post-treatments such as anodizing and passivation improve corrosion resistance while maintaining surface safety and cleanliness—crucial for medical applications.
E-Mobility and Smart Infrastructure
The e-mobility sector increasingly adopts Zamak die casting for connectors, housing units, and structural enclosures. The alloy’s recyclability and strength-to-weight ratio align perfectly with sustainability goals in electric vehicle design and charging infrastructure. By integrating prototyping services early in the product development process, manufacturers can reduce lead times and optimize resource efficiency before large-scale production.
Zamak’s inherent environmental friendliness—stemming from efficient energy use, recyclability, and minimal material waste—positions it as a vital material in advancing global sustainability initiatives across high-tech industries.