Can automation in metal stamping truly reduce overall production costs?
Introduction
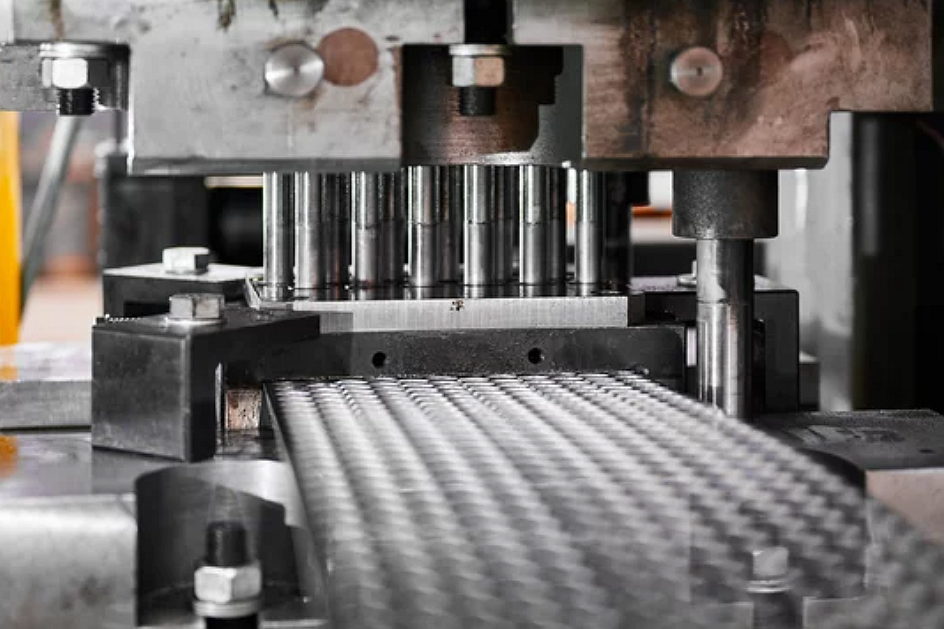
Automation has become a core driver of productivity and cost reduction in modern metal stamping operations. By integrating automated feeding, sensor-based quality monitoring, robotic handling, and rapid die‐change systems, manufacturers significantly improve throughput and minimize labor-dependent variation. Automation also enhances upstream processes, such as sheet metal fabrication and precision cutting steps like laser cutting. Integrated forming technologies, including metal bending, high-efficiency sheet metal stamping, and early-stage prototyping, all benefit from the consistency of automation, directly improving production economics.
How Automation Lowers Operational Costs
Labor Reduction and Increased Efficiency
Automated stamping lines reduce manual handling, allowing a single operator to supervise multiple presses. This reduces direct labor costs per part and shortens the cycle time. Industries like the automotive sector leverage automation to achieve high-volume output with minimal downtime. Telecommunication suppliers adopt automation to deliver components with tight tolerances at scale, while consumer electronics rely on automated forming for miniature, high-precision parts.
Reduced Scrap and Improved Repeatability
Material cost is a major factor in stamping economics, making scrap reduction essential. Automated monitoring systems detect misfeeds or dimensional deviations early, preventing the production of large batches of defective parts. High-value alloys like stainless steel and copper alloy particularly benefit from reduced waste. Automation also stabilizes forming behavior in materials such as carbon steel and lightweight metals like cast aluminum and zinc alloy.
Tooling Life Extension
Consistent feeding, optimized lubrication, and controlled press motion all contribute to reducing tooling wear. Automated alignment prevents off-center loads that could cause premature die damage. This extends the life and lowers the long-term maintenance cost. When combined with advanced forming processes such as precision casting or hybrid stamping–casting workflows, automation ensures highly predictable tool performance.
Impact on Post-Processing and Quality
Automation enables more consistent surfaces, reducing the need for downstream finishing. When finishing is required, parts transition seamlessly into treatments like powder coating or cosmetic improvement through anodizing. Fewer dimensional defects mean fewer reworks and lower total processing time.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Automated stamping lines stabilize production cost across large volumes. Although initial equipment investment is high, the reduction in labor, scrap, downtime, and tool replacement provides a rapid return on investment. For manufacturers operating in competitive industries, automation ensures predictable output, higher precision, and strong cost control.