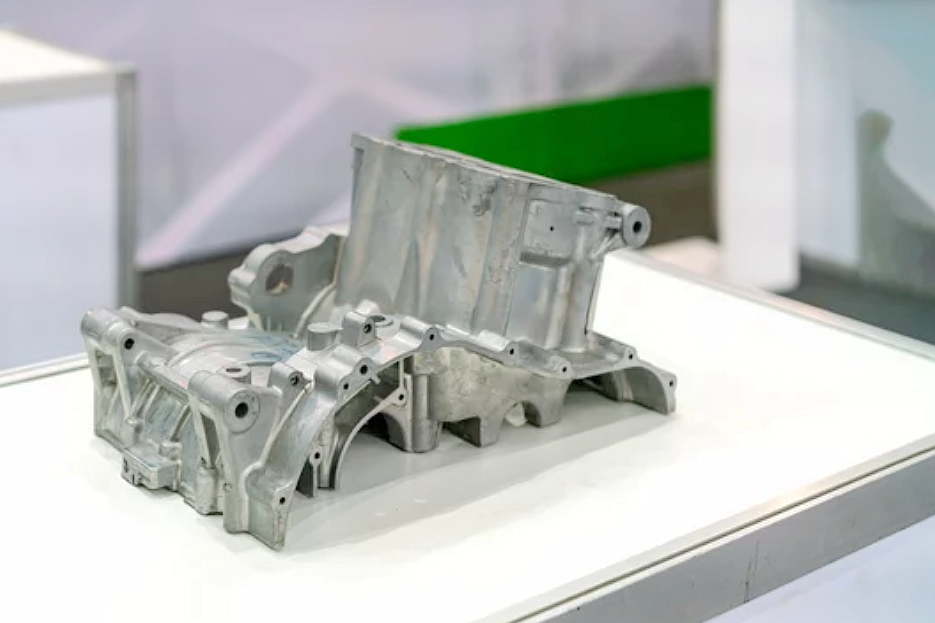
How does green sand casting reduce emissions and waste?
Closed-Loop Material Reuse
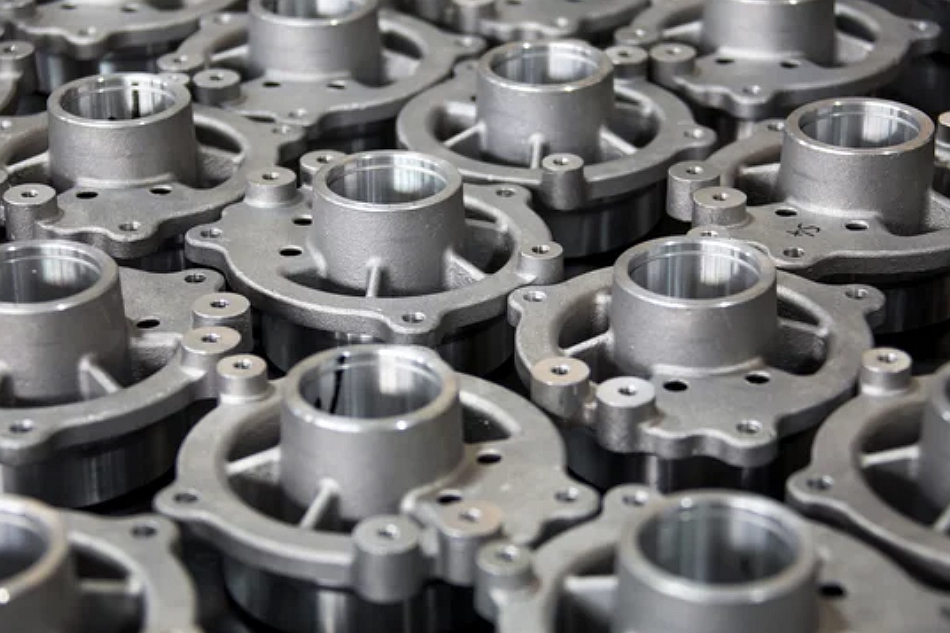
Green sand casting minimizes waste through its closed-loop sand reclamation system. The mixture of silica sand, bentonite clay, and water can be reused multiple times with minimal loss of performance. After each pour, spent sand is cooled, screened, and conditioned for the next mold cycle. This drastically reduces the amount of fresh sand required, lowering extraction-related environmental impact and landfill waste.
Binder and Additive Efficiency
Unlike chemical or resin-bonded molds used in other casting techniques, green sand systems employ natural binders and moisture, resulting in fewer volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The process eliminates harmful off-gassing during pouring and solidification, making it more environmentally friendly than processes such as investment casting or die casting, which often rely on synthetic resins or high-pressure systems.
Energy Conservation Through Temperature Control
Green sand molds can handle alloys like cast aluminum, cast iron, and zinc alloys at moderate pouring temperatures. This reduces melting energy requirements compared to refractory or permanent mold systems. Foundries that implement energy-efficient furnaces and optimized heat treatment cycles further decrease fuel consumption and CO₂ emissions.
Reduction of Casting Scrap and Rework
Process control improvements and simulation software allow engineers to predict solidification patterns accurately, minimizing shrinkage defects, inclusions, and porosity. This precision results in fewer rejected parts and less remelting of scrap metal, conserving energy and raw materials. Combined with as-machined finishes, it ensures optimal dimensional accuracy and minimal post-processing waste.
Environmentally Conscious Surface Treatments
Sustainable finishing options, such as powder coating and electropolishing, eliminate hazardous chemicals commonly found in traditional plating or solvent-based coatings. These finishes enhance corrosion resistance while maintaining compliance with environmental standards for industries like automotive and energy.
Dust and Emission Control Systems
Modern green sand foundries incorporate advanced air filtration, dust collection, and gas scrubbing systems. These units capture airborne particulates generated during molding, pouring, and shakeout, keeping emissions well below regulatory limits. Additionally, moisture-based sand systems naturally suppress dust generation compared to dry sand operations, thereby improving air quality and enhancing worker safety.
Integration of Circular Economy Practices
Green sand casting supports circular manufacturing principles by continuously reusing sand and metal feedstock. Offcuts and sprues are remelted for subsequent pours, while recovered sand is re-entered into the molding system. This closed-cycle production minimizes both solid and gaseous waste streams while supporting sustainable material management throughout the foundry.
Localized Resource Utilization
Because green sand uses easily available natural materials, local sourcing is feasible, reducing transport-related emissions. This approach enables manufacturers to maintain sustainable supply chains while meeting growing environmental compliance standards without compromising casting versatility or mechanical performance.