How does automation improve the efficiency of metal stamping operations?
Introduction
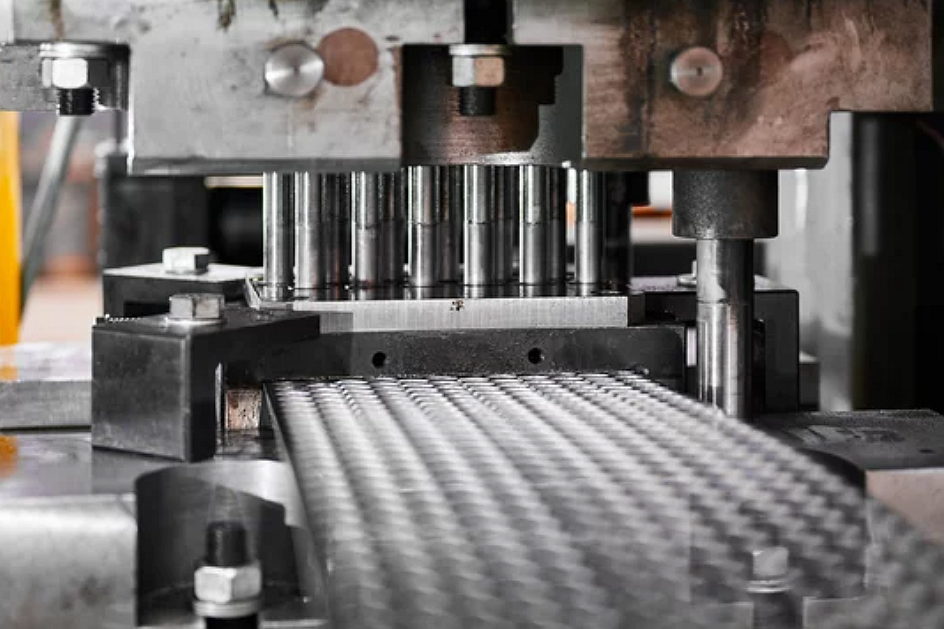
Automation has become a core driver of efficiency in metal stamping, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher output, better precision, and more consistent part quality. Automated systems integrate seamlessly with upstream and downstream manufacturing processes such as sheet metal stamping, laser cutting, metal bending, prototyping, and CNC machining prototyping. By reducing manual handling and increasing repeatability, automation transforms stamping into a more scalable and cost-controlled process for industries with demanding volume requirements.
Enhanced Speed and Throughput
Automated feed systems, robotic loading, and real-time press control dramatically increase production speed. Metal coils are fed continuously, and the system maintains optimal press timing to avoid delays. This high-speed workflow is particularly valuable for sectors such as the automotive industry, where thousands of stamped components are produced per hour. In consumer electronics, automation supports the production of miniaturized, thin-gauge parts that require consistent forming at rapid cycle times. For telecommunication applications, automation ensures stable quality in high-volume connector and shielding components.
Improved Dimensional Accuracy and Consistency
Modern stamping automation includes closed-loop sensors that monitor pressure, speed, die alignment, and material thickness. These automated checks help maintain predictable dimensional accuracy and reduce variations that typically arise in manual operations. Choosing suitable materials—such as carbon steel, stainless steel, copper alloy, cast aluminum, or engineering plastics like ABS—also contributes to stable automated forming due to predictable mechanical behavior.
Lower Operating Costs
Automation reduces labor demand during continuous production and minimizes downtime caused by manual feeding errors or improper part handling. When paired with upstream operations such as precision coil preparation or downstream finishing processes like powder coating or anodizing, automated lines operate with fewer disruptions and reduced rework rates. This results in lower per-part manufacturing costs and improved overall equipment effectiveness.
Improved Worker Safety and Operational Stability
Stamping presses operate with high force and speed. Automation removes operators from hazardous zones by using robotic systems for material feeding, part extraction, and die maintenance. Automated monitoring also detects anomalies early—such as feed misalignment or die wear—preventing costly damage and unscheduled downtime.
Scalability for High-Volume Programs
Automation enables consistent cycle times and predictable quality, which are crucial for sustaining long-term, high-volume stamping programs. The capability to integrate progressive dies, transfer systems, automated inspection, and adaptive press controls allows manufacturers to achieve stable production for millions of components while reducing scrap and tool wear.
Conclusion
Automation enhances metal stamping by increasing output speed, improving accuracy, lowering operating costs, and strengthening safety. When supported by the right materials, finishing processes, and upstream manufacturing technologies, automation transforms stamping operations into reliable, scalable, and highly cost-effective production systems.