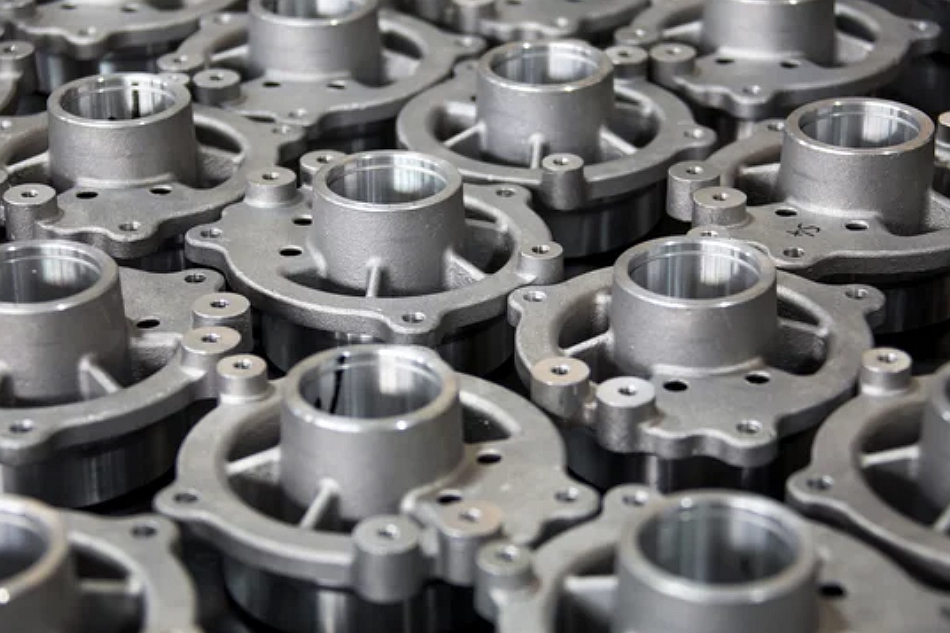
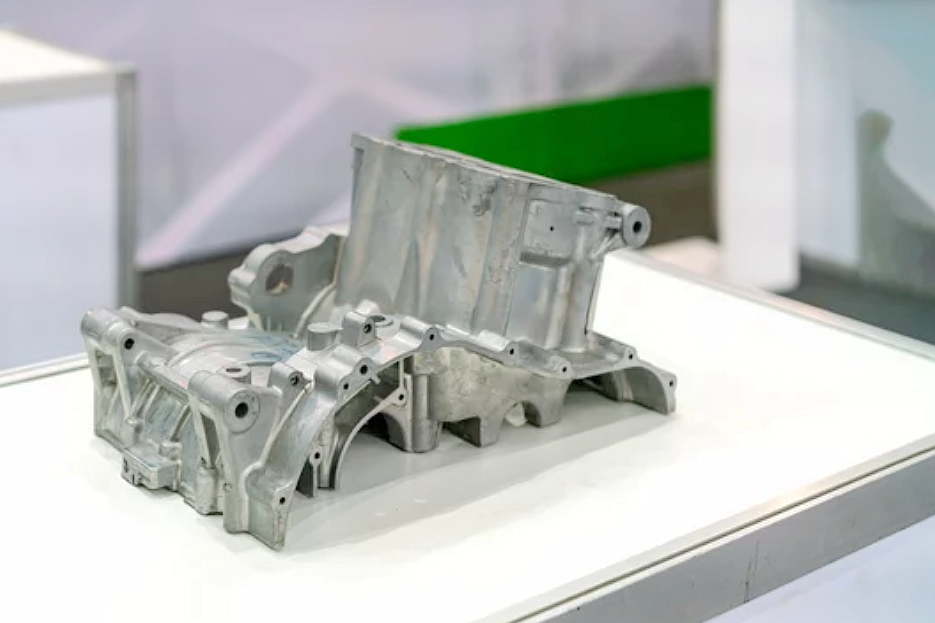
What makes sand casting environmentally sustainable?
Recyclable Molding Materials
One of the key environmental advantages of sand casting is its ability to reuse molding sand multiple times. The silica or olivine sands used in the process can be reclaimed and recycled with minimal degradation through proper screening and binder regeneration. This significantly reduces waste generation and conserves raw materials compared to other foundry methods.
Energy Efficiency and Alloy Compatibility
Sand casting supports a wide range of materials, including cast aluminum, cast iron, and copper alloys, allowing manufacturers to optimize for alloys with lower melting temperatures. Using lightweight materials such as A356 aluminum also reduces overall energy consumption during melting and solidification. When combined with modern furnace systems and controlled cooling, this improves thermal efficiency and decreases CO₂ emissions.
Reduction of Material Waste
The sand casting process produces minimal excess metal due to the precision of its gating and riser design. Furthermore, leftover sand, dross, and sprues can be remelted or repurposed in subsequent batches. Compared to high-pressure processes such as aluminum die casting, sand casting’s low tooling requirements and flexibility reduce the need for frequent mold replacement, cutting down on material and energy use.
Environmentally Friendly Surface Finishes
Eco-conscious surface finishing further enhances sustainability. Finishes such as powder coating and anodizing offer non-toxic, VOC-free protection for aluminum castings. These coatings extend the life of components without harmful solvents or plating baths, aligning with modern environmental standards for the energy and automotive industries.
Process Optimization and Emission Control
Through modern foundry automation and efficient binder systems, emissions from organic binders and core gases are significantly reduced. Implementing heat treatment and sand reclamation systems enables a closed-loop operation, minimizing airborne particulates and improving worker safety. Many advanced foundries integrate dust collection and gas treatment units to meet ISO 14001 environmental management standards.
Reusability and Circular Manufacturing
Sand casting is inherently aligned with circular manufacturing principles. Since sand molds and metal scrap can both be reintroduced into the production cycle, it supports sustainable resource use. This makes sand casting a practical solution for large components in industries such as energy, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where recyclability and lifecycle impact are critical factors.
Localized and Low-Impact Production
Due to its flexibility, sand casting can be performed using locally sourced sands and alloys, thereby reducing transportation emissions and the associated carbon footprint. It also requires lower capital and infrastructure investment, making it suitable for regional, small-batch, and custom part manufacturing with reduced environmental overhead.
Sustainable Future Outlook
With continuous improvements in molding materials, emission control, and process automation, the environmental footprint of sand casting is continually decreasing. By combining efficient alloy selection, advanced reclamation systems, and eco-friendly surface finishing, modern sand foundries make significant contributions to the global shift toward sustainable manufacturing.