Which industries commonly use custom Zamak die casting?
Introduction
Custom Zamak die casting provides exceptional design freedom, dimensional accuracy, and cost efficiency, making it a vital process across numerous industrial sectors. Zamak’s combination of a low melting temperature, excellent flowability, and high surface finish enables engineers to produce durable, aesthetically pleasing, and functional parts that meet diverse market needs. Below are the primary industries leveraging this versatile technology.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry remains one of the largest consumers of Zamak die-cast parts. Components such as door handles, brackets, and interior trim are often made from Zamak 3 or Zamak 5 due to their superior strength, wear resistance, and plating compatibility. These alloys also support thin-walled structures with intricate details that reduce vehicle weight while maintaining rigidity.
The integration of gravity casting and CNC machining prototyping enables automotive engineers to refine geometries before mass production. After casting, finishes like chrome plating or black oxide coating enhance appearance and corrosion resistance, aligning with high aesthetic and performance standards.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, Zamak die casting enables the production of sleek, high-quality housings and frames that meet tight tolerances and deliver a premium tactile experience. The process enables the creation of ergonomic and compact components, such as smartwatch bezels, smartphone housings, and camera bodies.
For applications requiring a fine surface texture, Zamak 7 is preferred due to its excellent fluidity and finish. Surface processes, such as powder coating or electroplating, further enhance visual quality and protect against oxidation. The combination of durability, lightweight performance, and aesthetic adaptability makes Zamak ideal for precision consumer products.
Locking and Security Systems
The locking system sector benefits immensely from Zamak’s dimensional stability and hardness. High-precision parts such as lock housings, cylinders, and keys require micron-level accuracy to ensure smooth operation and long-term security.
Zamak’s strength enables tight tolerances and mechanical integrity in complex assemblies, often enhanced through insert molding, which embeds metallic cores or plastic inserts. The combination of precision casting and plating provides parts that resist tampering and environmental degradation while maintaining a professional finish.
Medical and Precision Instruments
In the medical device field, Zamak die casting enables the production of compact, corrosion-resistant components, including diagnostic housings, control knobs, and connectors. Its ability to form precise threads and smooth surfaces makes it compatible with sterilization environments.
When combined with powder compression molding or ceramic injection molding (CIM), hybrid assemblies achieve greater mechanical and thermal performance. Optional passivation ensures biocompatibility and extended life under medical-grade conditions.
Lighting and Electrical Applications
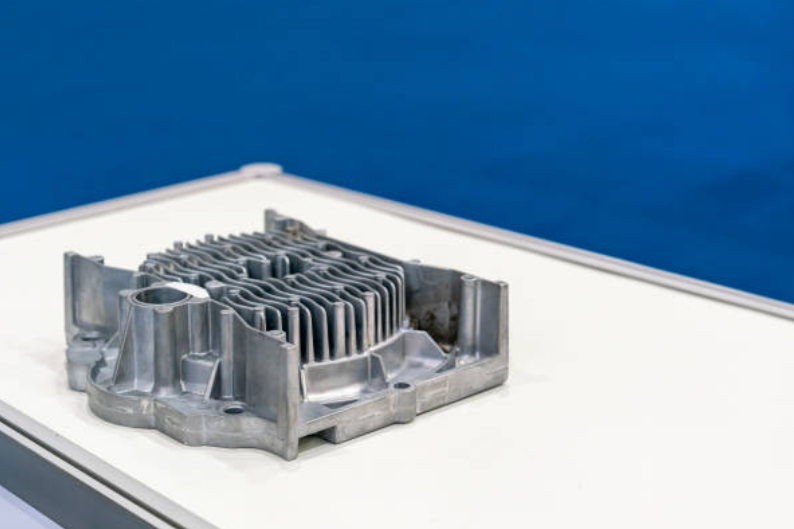
Zamak alloys are also integral to lighting solutions and telecommunication products where heat dissipation, strength, and fine detailing are required. Housings, heat sinks, and connectors benefit from Zamak’s high conductivity and dimensional stability. The integration with sheet metal fabrication provides designers flexibility to merge functional strength with compact layouts for modern lighting and telecom designs.
Conclusion
From automotive assemblies to medical devices, Zamak die casting enables efficient production of parts that meet strict mechanical, visual, and environmental demands. Its compatibility with multiple surface treatments and materials ensures it remains a cornerstone technology in precision manufacturing.