Tough as Nails: How Over Molding Fortifies Products Against Life’s Knocks
Introduction
Consumers and industries expect products that can withstand life's inevitable knocks and impacts in today's demanding market. Overmolding has become a revolutionary manufacturing method, significantly boosting product durability, resilience, and longevity. By strategically combining rigid substrates with softer, impact-resistant materials, manufacturers create products that are better equipped to withstand physical stress, environmental wear, and daily usage, thereby meeting stringent durability expectations across industries such as consumer electronics and the automotive sector.
Understanding Overmolding
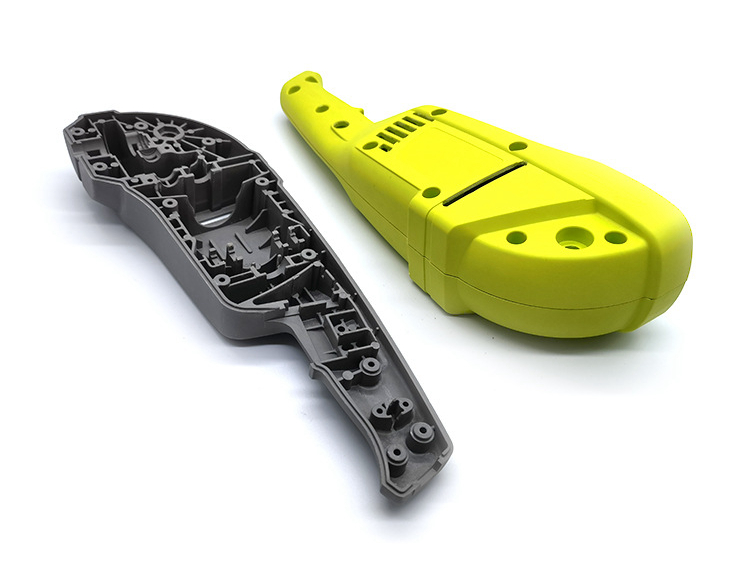
Overmolding is a specialized plastic injection molding process in which a rigid base substrate is enveloped by a softer, protective material. This integration combines structural strength with flexible outer layers, significantly enhancing performance characteristics such as impact resistance and ergonomic comfort.
Types of Materials Used in Overmolding:
Rubbers: Deliver exceptional shock absorption and water resistance.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Provide flexibility, grip, and durability.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): Known for superior abrasion resistance and toughness.
Silicones: Highly biocompatible and ideal for medical and food-safe applications.
Overmolding involves producing the rigid substrate first, then injecting a softer, durable material, such as TPU or TPE, to create a robust bond between the layers.
Benefits of Overmolding in Enhancing Product Durability
Increased Impact Resistance and Shock Absorption
Overmolding dramatically improves a product's ability to absorb impacts and resist shocks. Materials such as TPE and TPU distribute force efficiently, significantly reducing the risk of damage and enhancing the longevity of durable consumer products.
Enhanced Grip and Ergonomic Comfort
Products featuring overmolded grips offer ergonomic advantages, reducing user fatigue and enhancing handling. The soft-touch materials ensure superior comfort, which is particularly beneficial in handheld power tools and electronic devices that are frequently subject to prolonged use.
Improved Resistance to Environmental Factors
Overmolding protects against environmental stress, including exposure to water, chemicals, UV rays, and extreme temperatures. This environmental resistance is crucial in demanding applications such as automotive interiors and industrial equipment.
Extension of Product Lifespan
By offering robust protection against physical and environmental stresses, overmolding significantly extends product lifecycles. Enhanced durability reduces maintenance, lowers replacement costs, and elevates customer satisfaction, positioning products favorably in competitive markets.
Selecting the Right Materials for Overmolding
Selecting the appropriate overmolding materials is crucial for optimizing product performance. Compatibility between substrate materials and overmold materials ensures strong bonding and overall durability.
Popular Overmolding Materials and Benefits:
TPE: Ideal for consumer electronics due to flexibility, comfort, and chemical resistance.
TPU: Excellent abrasion resistance and toughness for industrial and automotive applications.
Silicone: Preferred in medical device manufacturing and kitchenware due to its biocompatibility, hygiene, and high-temperature resistance.
Factors Influencing Material Selection:
Performance Requirements: Evaluate necessary impact resistance, flexibility, and environmental resilience.
Cost: Balance between material performance and budget constraints.
Aesthetics: Desired texture and appearance influencing consumer perception and acceptance.
Real-World Examples and Industry Applications
Consumer Electronics
Overmolding is widely used in electronics, including smartphones and wearable devices. Products with TPU or TPE protective casings offer superior impact resistance, shock absorption, and ergonomic comfort, which are essential for daily use and protection against accidental drops.
Industrial Tools and Equipment
Many power tools and handheld equipment utilize overmolded handles, which reduce vibration and improve user safety and comfort. Industrial devices, such as drills, saws, and impact drivers, benefit significantly from durable, shock-resistant grips provided by overmolding.
Automotive Applications
Automotive interiors often utilize overmolding for components like dashboard controls, gear shifters, and knobs. Materials like TPE and silicone improve durability, aesthetics, and ergonomic comfort, aligning with stringent automotive quality standards.
Key Considerations for Successful Overmolding
Designing for Optimal Adhesion
Achieving strong adhesion between substrates and over-molding materials requires careful material selection, precise mold design, and optimized injection molding parameters. Proper bonding ensures long-lasting product performance.
Common Challenges
Material Incompatibility: Poor adhesion due to incompatible substrate and over-molding materials.
Bonding Issues: Delamination arising from incorrect mold temperatures or inadequate surface treatments.
Solutions and Best Practices
Conduct thorough compatibility testing before manufacturing.
Optimize molding conditions, including mold temperature, pressure, and injection speed.
Use adhesion promoters or surface treatments when necessary to improve bonding.
Future Trends and Innovations in Overmolding
Advancements in Sustainable Overmolding Materials
Environmental awareness is accelerating innovations in sustainable and biodegradable overmolding materials. New bio-based elastomers and recyclable compounds offer eco-friendly alternatives that do not compromise durability or performance.
Emerging Technologies
Automation, robotics, and real-time monitoring technologies are increasingly optimizing overmolding processes. Advanced manufacturing solutions enhance production efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness, further solidifying the manufacturing value of overmolding.
Predicted Trends and Market Growth
Overmolding is expected to experience significant growth, particularly in the automotive, consumer electronics, and healthcare sectors. The increased emphasis on sustainability and advanced materials will continue to enhance its appeal, driving adoption and market expansion.
Conclusion
Overmolding technology empowers manufacturers to produce resilient products that effectively withstand life's inevitable knocks and bumps. Manufacturers can deliver superior-quality, durable, and ergonomically comfortable products by strategically selecting suitable materials and optimizing production processes.
Businesses seeking to enhance market competitiveness and customer satisfaction should leverage overmolding to fortify their products, meeting the rising expectations of consumers for durability and resilience.