What challenges do manufacturers face when adopting sustainable gravity casting?
Overview
Transitioning to sustainable gravity casting requires striking a balance between environmental responsibility and technical and economic feasibility. While the approach reduces carbon footprint and waste, manufacturers must overcome significant process, material, and regulatory challenges to achieve consistent performance and sustainability goals simultaneously.
Manufacturing Process Challenges
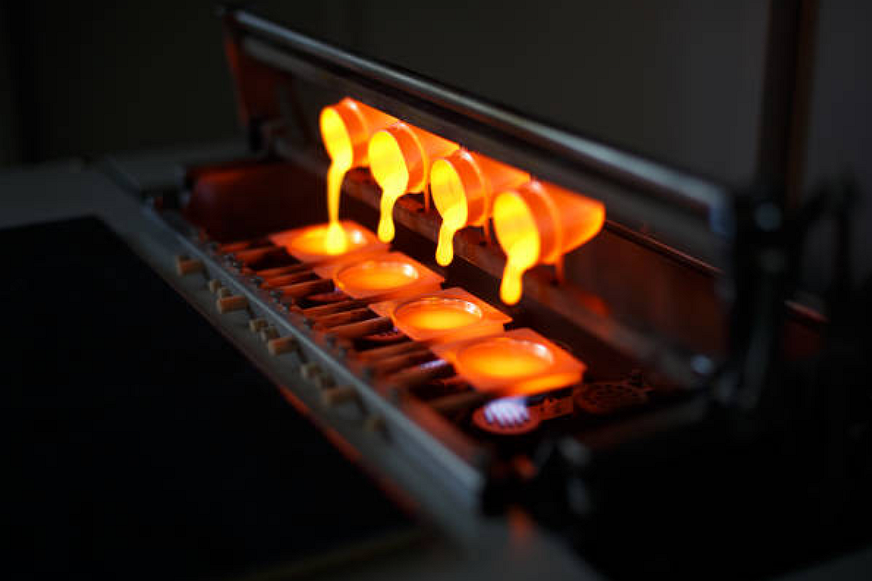
Integrating sustainability into the gravity casting process demands precision and process control. Implementing CNC machining prototyping enables tighter mold tolerances, yet it also increases upfront equipment costs. Similarly, sand casting is often used for prototype validation but can produce variable surface finishes if sand reuse systems are not optimized. Moreover, adopting advanced automation and sheet metal fabrication integration for lightweight hybrid designs requires significant training and capital investment. Manufacturers must also address the energy intensity of preheating molds and melting operations, often by shifting to renewable or waste-heat recovery systems through smart foundry layouts and investment casting refinements.
Material Availability and Compatibility
A core sustainability barrier lies in sourcing eco-friendly, recyclable materials with reliable mechanical performance. Recycled cast aluminum can introduce impurities that degrade fatigue strength. Likewise, magnesium alloys are lightweight but reactive, requiring controlled atmospheres to prevent oxidation. The use of nickel-based alloys in high-temperature components presents challenges due to their hardness, which can lead to cost and machining difficulties. Balancing recyclability, castability, and durability often requires blending multiple alloy systems and refining melt treatments to achieve stable microstructures.
Surface Treatment Limitations
Eco-conscious finishing is another technical challenge. Traditional coatings often rely on heavy metals and solvents, which conflict with sustainability principles. Transitioning to clean, durable finishes such as anodizing and powder coating reduces emissions but demands advanced process control to achieve uniform adhesion and color stability. These greener coatings may also require specific substrate preparation and post-cure temperatures, which can impact throughput.
Industrial Implementation and Economic Barriers
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy sectors are under increasing pressure to comply with carbon-reduction regulations and life-cycle assessment standards. Yet, the lack of unified sustainability certification systems for casting creates uncertainty in investment returns. Establishing closed-loop recycling programs and implementing energy-monitoring systems also adds operational complexity and necessitates cross-supply chain collaboration.
Ultimately, adopting sustainable gravity casting is not a simple technological upgrade—it involves rethinking design, sourcing, and process philosophy to meet performance expectations under lower environmental impact.