How do technological advancements improve Zamak casting precision?
Introduction to Modern Zamak Precision Casting
Zamak alloys remain a cornerstone of zinc die casting, offering exceptional flow characteristics and detail reproduction. As industries demand tighter tolerances and more complex geometries, technological advancements in casting processes, materials, and quality control have significantly improved Zamak’s dimensional precision and performance consistency.
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
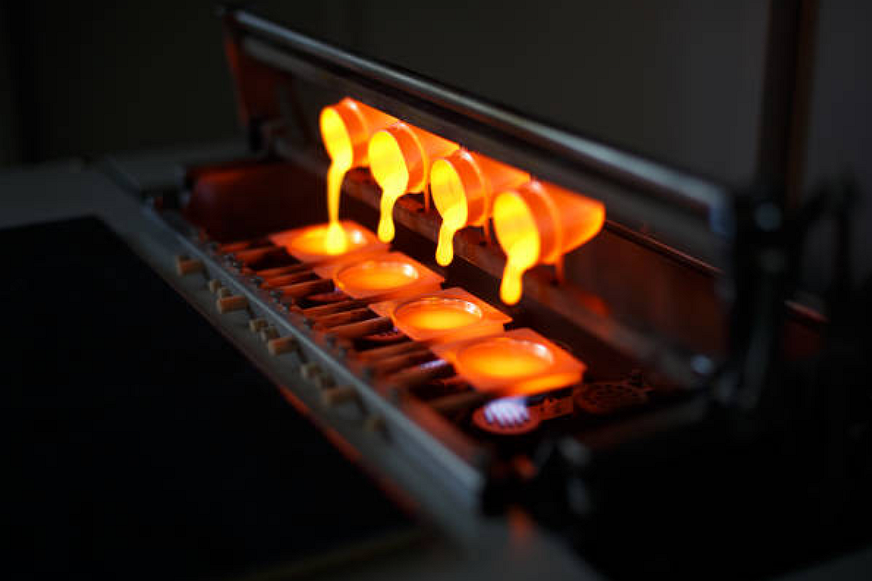
Precision begins with optimized tooling and mold design. Modern pressure die casting machines now feature servo-controlled injection systems, providing accurate metal flow and pressure regulation. This allows engineers to minimize porosity and dimensional variation. When combined with CNC machining prototyping and rapid molding prototyping, manufacturers can validate part geometry and casting feasibility before full-scale production.
Additionally, innovations in gravity casting help create uniform wall thickness and reduce turbulence during metal filling, enabling smoother microstructures. The integration of sheet metal fabrication with die casting also supports the creation of hybrid assemblies with precision alignment between cast and formed components.
Surface Treatment Technologies Elevating Performance
Advanced coatings play a vital role in maintaining precision and durability. High-quality electroplating provides uniform layer thickness while protecting against corrosion, whereas powder coating improves part appearance without compromising dimensional stability. These surface technologies not only extend component lifespan but also help sustain critical tolerances under operational stress and thermal cycling.
Improved Material Science and Alloy Engineering
The precision of Zamak casting depends heavily on alloy uniformity. Modern metallurgical control enables the refinement of compositions for Zamak 3, Zamak 5, and Zamak 7, thereby minimizing impurities that can cause shrinkage or microcracks. For enhanced mechanical properties, the hybrid use of magnesium alloy or cast aluminum can deliver lighter components with higher strength-to-weight ratios. In precision assemblies, nickel-based alloys or stainless steel inserts are integrated to achieve dimensional reinforcement where required.
Real-Time Monitoring and Automation
Smart foundries now employ digital sensors and process analytics for real-time monitoring of injection pressure, melt temperature, and solidification rate. Automated systems detect deviations instantly, enabling corrective action during production rather than after inspection. These improvements, along with 3D scanning and in-line coordinate measuring systems, significantly reduce rework rates and maintain repeatability in precision-critical industries.
Applications Across Industries
In the automotive industry, tighter process control ensures the consistent production of housing components and gear mechanisms. The consumer electronics sector benefits from micro-precision enclosures that require flawless surface aesthetics. Similarly, locking systems utilize high-precision Zamak castings to guarantee secure mechanical engagement under prolonged wear. These industry applications exemplify how technological integration is redefining what Zamak can achieve.
Engineering Outlook
With continued advancements in process simulation, material innovation, and automation, Zamak die casting has entered an era where micron-level accuracy is attainable at a mass-production scale. As machine learning and digital twins evolve, predictive quality control will further minimize human error and variability, ensuring Zamak maintains its dominance in precision metal manufacturing.